Rheumatological Disease/Ankylosing spondylitis
The most common rheumatological diseases of the spine are:
- Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew disease)
- Chronic Polyarthritis (Rheumatoid arthritis)
Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew disease)
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic rheumatic inflammation. It typically affects hinges and tendon insertions at the bones. The spine as well as the sacroiliac joints are mostly implicated by the inflammation. The sacroliliac joints connect the spine to the pelvis. The disease proceeds in thrusts, including nightly pain and morning stiffness of the spine. In time, the intervertebral joints and discs as well as the vertebral ligaments start to ossify, leading to an incremental stiffening of the spine. In an advanced state, the spine stiffens and ossifies in a kyphotic position.
Treatment
The main goal of treatment is to ease the patient’s pain and maintain the mobility of the spine. Conservative treatment and diagnostics are part of the rheumatologists expertise.
Operation
If the spine has stiffened in a kyphotic position, the patients have a hard time standing upright and getting a horizontal view. Not only does this cause chronic pain, but a significant reduction in their quality of life. Such a situation can be improved with a straightening operation.
Straightening operation
In the course of this procedure, a gore is cut out of the vertebral body (osteotomy) and the spine is put together in such a way, that it is straight and upright in the desired position.
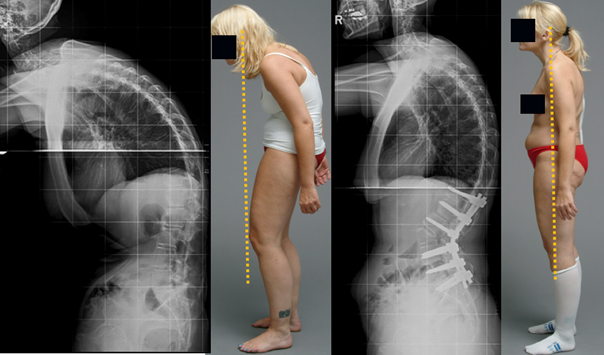
Example 1: Erection of a severe kyphosis caused by ankylosoing spondylitis by means of an osteotomy in the lumbar spine
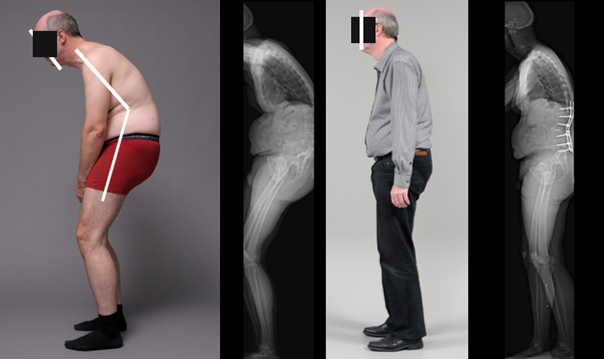
Example 2: Significant normalisation of standing position and field of vision following straightening surgery in a patient with Morbus Bechterew
Chronic polyarthritis (rheumatoid arthritis)
In chronic polyarthritis, multiple joints are affected by chronic inflammation. Concerning the spine, the most commonly affected joints are those connecting head and neck. This leads to instability, narrowing of the spinal canal and compression of the spinal cord.
Operation
During surgery, the spinal cord is decompressed and the upper cervical spine and the head are stabilised.
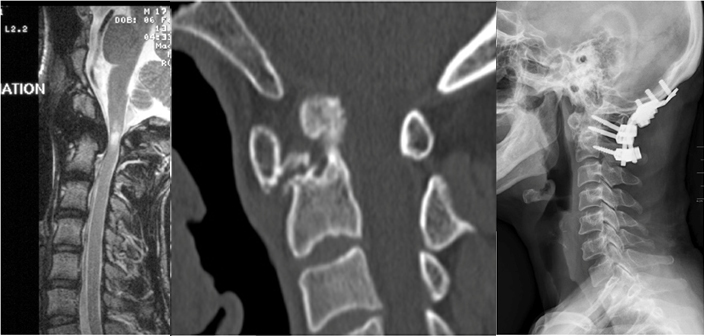
Example: Chronic polyarthritis severely affecting the connection between head and neck. Stabilisation using implants
